Glossary term: 星雲
Description: 星雲是一種遙遠的天體,具有雲的外觀。通常,星雲由星際氣體和塵埃組成。在歷史上,星雲一詞指的是所有延展的、邊緣模糊的天體,包括我們今天所認識的星系--像銀河系這樣的遙遠恆星系統。如今,星雲一詞僅限於指代星際介質中的氣體和塵埃雲,即星系內恆星之間的氣體和塵埃。星雲被分為許多不同的種類:分子雲相對較冷,顏色較暗,主要由分子氫組成;新的恆星就是在這樣的雲中形成的。巨型分子雲可以包含多達數百萬個太陽質量的氫氣。年輕恆星頻繁地噴射出狹窄的電離氣體噴流;當這些噴流激發周圍的氣體時,就會形成一種叫做赫比-哈羅(Herbig–Haro)天體的星雲。當大質量恆星形成後,它們的強烈輻射會使周圍的氣體髮出特徵性的紅光;這種由熾熱的電離氫氣組成的星雲被稱為 HII 區(電離氫區)。其他類型的星雲與恆星的死亡有關:低質量恆星的死亡會留下不斷膨脹的氣體外殼,這種星雲(命名上有些令人困惑)被稱為行星狀星雲。當大質量恆星以超新星的形式爆發時,噴出的氣體會形成一種叫做超新星遺跡的星雲。
Related Terms:
See this term in other languages
Term and definition status: The original definition of this term in English have been approved by a research astronomer and a teacher The translation of this term and its definition is still awaiting approval
This is an automated transliteration of the simplified Chinese translation of this term
The OAE Multilingual Glossary is a project of the IAU Office of Astronomy for Education (OAE) in collaboration with the IAU Office of Astronomy Outreach (OAO). The terms and definitions were chosen, written and reviewed by a collective effort from the OAE, the OAE Centers and Nodes, the OAE National Astronomy Education Coordinators (NAECs) and other volunteers. You can find a full list of credits here. All glossary terms and their definitions are released under a Creative Commons CC BY-4.0 license and should be credited to "IAU OAE".
If you notice a factual or translation error in this glossary term or definition then please get in touch.
Related Diagrams
人馬座星圖
Credit: 國際天文學聯合會天文教育辦公室(IAU OAE)根據國際天文學聯合會和《天空與望遠鏡》的原文改編
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons 姓名標示 4.0 國際 (CC BY 4.0) icons
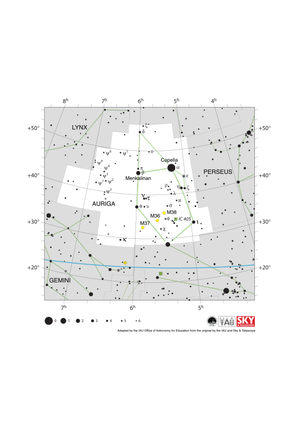
Auriga Constellation Map
Credit: Adapted by the IAU Office of Astronomy for Education from the original by the IAU and Sky & Telescope
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons 姓名標示 4.0 國際 (CC BY 4.0) icons
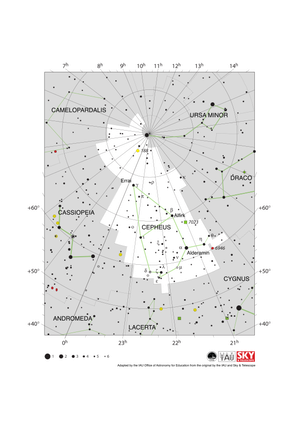
Cepheus Constellation Map
Credit: Adapted by the IAU Office of Astronomy for Education from the original by the IAU and Sky & Telescope
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons 姓名標示 4.0 國際 (CC BY 4.0) icons
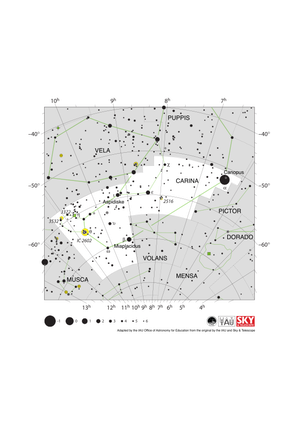
Carina Constellation Map
Credit: Adapted by the IAU Office of Astronomy for Education from the original by the IAU and Sky & Telescope
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons 姓名標示 4.0 國際 (CC BY 4.0) icons
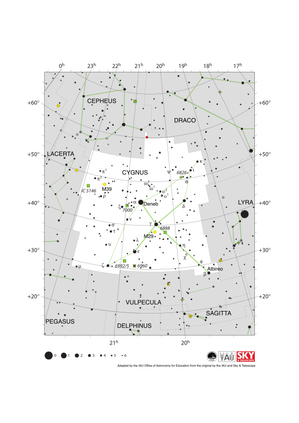
Cygnus Constellation Map
Credit: Adapted by the IAU Office of Astronomy for Education from the original by the IAU and Sky & Telescope
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons 姓名標示 4.0 國際 (CC BY 4.0) icons
Related Activities
Reading the Rainbow
astroEDU educational activity (links to astroEDU website) Description: By understanding how rainbows work, you can discover about light and its properties, learning about stars, nebulae, galaxies, and our Universe.
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons 姓名標示 4.0 國際 (CC BY 4.0) icons
Age Ranges:
14-16
, 16-19
, 19+
Education Level:
Informal
, Middle School
, Secondary
, University
Areas of Learning:
Interactive Lecture
, Observation based
, Social Research
Costs:
Low Cost
Duration:
1 hour 30 mins
Group Size:
Group
Skills:
Analysing and interpreting data
, Asking questions
, Engaging in argument from evidence