Glossary term: 銀河系
Description: 銀河系是太陽系所在的星系。它由大約 1000-4000 億顆恆星組成。太陽系距離銀河系中心約 26600 光年。在夜空中,我們可以看到它像一條微弱的帶子延伸至整個天空,其中心位於人馬座。
銀河系是一個相對較大的棒狀螺旋星系,其中恆星的分布沿著厚度約為1000光年的盤面延伸到約10萬光年處。銀河系盤形成於 80 到 100 億年前。
銀河系盤的周圍環繞著稀疏得多的恆星暈,其中包括球狀星團。這些球狀星團是銀河系中最古老的天體,年齡約為 125 億年。除了恆星,銀河系還由星際介質的氣體和塵埃以及暗物質組成。星際介質主要局限於星盤,而周圍的暗物質暈則比恆星光環延伸得更遠。
銀河系中心有一個超大質量黑洞,其質量約為太陽的 400 萬倍。銀河系中心附近有一個星系核,其中大部分是較老的恆星,它們向一個方向伸長,形成一個棒狀。
Related Terms:
See this term in other languages
Term and definition status: The original definition of this term in English have been approved by a research astronomer and a teacher The translation of this term and its definition is still awaiting approval
This is an automated transliteration of the simplified Chinese translation of this term
The OAE Multilingual Glossary is a project of the IAU Office of Astronomy for Education (OAE) in collaboration with the IAU Office of Astronomy Outreach (OAO). The terms and definitions were chosen, written and reviewed by a collective effort from the OAE, the OAE Centers and Nodes, the OAE National Astronomy Education Coordinators (NAECs) and other volunteers. You can find a full list of credits here. All glossary terms and their definitions are released under a Creative Commons CC BY-4.0 license and should be credited to "IAU OAE".
If you notice a factual or translation error in this glossary term or definition then please get in touch.
Related Media
伊朗盧特沙漠上空的銀河拱門,作者 Amirreza Kamkar,伊朗(伊斯蘭共和國)
Credit: Amirreza Kamkar/IAU OAU
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons 姓名標示 4.0 國際 (CC BY 4.0) icons
世界各處的星座
Credit: Stephanie Ye Ziyi/IAU OAE
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons 姓名標示 4.0 國際 (CC BY 4.0) icons
流動的夜空
Credit: Robert Barsa/IAU OAE
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons 姓名標示 4.0 國際 (CC BY 4.0) icons
智利的夜空
Credit: Robert Barsa/IAU OAE
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons 姓名標示 4.0 國際 (CC BY 4.0) icons
南天
Credit: 戴建峰/國際天文學聯合會教育辦公室
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons 姓名標示 4.0 國際 (CC BY 4.0) icons
Related Diagrams
人馬座星圖
Credit: 國際天文學聯合會天文教育辦公室(IAU OAE)根據國際天文學聯合會和《天空與望遠鏡》的原文改編
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons 姓名標示 4.0 國際 (CC BY 4.0) icons
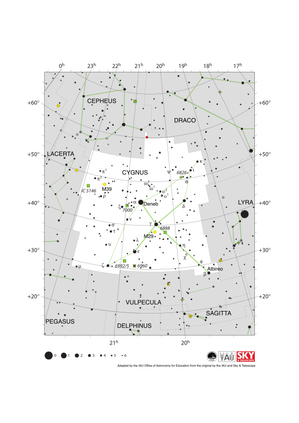
Cygnus Constellation Map
Credit: Adapted by the IAU Office of Astronomy for Education from the original by the IAU and Sky & Telescope
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons 姓名標示 4.0 國際 (CC BY 4.0) icons
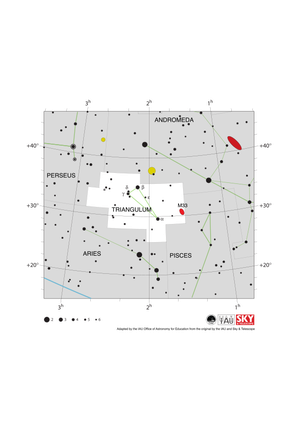
Triangulum Constellation Map
Credit: Adapted by the IAU Office of Astronomy for Education from the original by the IAU and Sky & Telescope
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons 姓名標示 4.0 國際 (CC BY 4.0) icons
Related Activities
Glitter Your Milky Way
astroEDU educational activity (links to astroEDU website) Description: Explore the Milky Way and characteristics of galaxies using glitter drawing.
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons 姓名標示 4.0 國際 (CC BY 4.0) icons
Tags:
Art
, Creativity
, Hands-on
, Handcraft
Age Ranges:
6-8
, 8-10
Education Level:
Middle School
, Primary
Areas of Learning:
Fine Art focussed
Costs:
Medium Cost
Group Size:
Group
Skills:
Communicating information
Living in the Milky Way
astroEDU educational activity (links to astroEDU website) Description: Build a model of the Milky Way to discover what our galaxy contains.
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons 姓名標示 4.0 國際 (CC BY 4.0) icons
Tags:
Hands-on
, Model
Age Ranges:
6-8
, 8-10
Education Level:
Primary
Areas of Learning:
Problem-solving
, Social Research
Costs:
Medium Cost
Duration:
1 hour 30 mins
Group Size:
Group
Skills:
Asking questions
, Communicating information
, Developing and using models