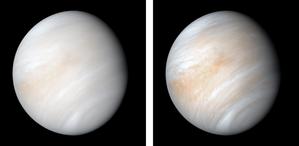
Glossarbegriffe: Venus (Planet)
Description: Die Venus ist der zweitnächste Planet zur Sonne. Sie wird oft als Zwilling der Erde bezeichnet und ist ein erdähnlicher Gesteinsplanet mit einem Radius von etwas mehr als 6.000 Kilometern (km), was etwa 95 % des Erdradius entspricht. Ihre Masse beträgt das 0,815-fache der Masse der Erde. Die Atmosphäre der Venus ist 90 Mal dichter als die der Erde. Sie besteht hauptsächlich aus Kohlenstoffdioxid und dicken Wolken aus Schwefelsäure, die die gesamte Oberfläche einhüllen. Die dichte Atmosphäre bewirkt einen sehr starken Treibhauseffekt, der zu einer Oberflächentemperatur von 460 Grad Celsius führt.
Die durchschnittliche Entfernung der Venus von der Sonne beträgt 108 Millionen Kilometer, was etwa 0,72 Astronomischen Einheiten entspricht (Abstand Erde-Sonne). Sie braucht 224,7 Tage für eine Umrundung. Die Venus braucht sehr lange, um sich einmal um ihre Achse in Bezug auf den Fixsternhintergrund zu drehen: Ein solcher Venustag entspricht 243 Erdtagen. Dies ist länger als die Zeit, die die Venus für einen Umlauf um die Sonne benötigt. Die Venus hat keine bekannten Monde.
Die Venus ist nach der römischen Göttin der Liebe benannt. Da sich die Venus so nahe bei der Sonne befindet, ist sie oft kurz vor Sonnenaufgang oder nach Sonnenuntergang am Nachthimmel zu sehen. Bei diesen Gelegenheiten ist die Venus auch mit bloßem Auge auffallend hell und wird traditionell als Morgenstern bzw. Abendstern bezeichnet. Mit einem Fernglas kann man sehen, dass die Venus ähnliche Phasen wie der Mond hat.
Zugehörige Glossarbegriffe:
See this term in other languages
Term and definition status: The original definition of this term in English have been approved by a research astronomer and a teacher The translation of this term and its definition is still awaiting approval
The OAE Multilingual Glossary is a project of the IAU Office of Astronomy for Education (OAE) in collaboration with the IAU Office of Astronomy Outreach (OAO). The terms and definitions were chosen, written and reviewed by a collective effort from the OAE, the OAE Centers and Nodes, the OAE National Astronomy Education Coordinators (NAECs) and other volunteers. You can find a full list of credits here. All glossary terms and their definitions are released under a Creative Commons CC BY-4.0 license and should be credited to "IAU OAE".
Zugehörige Medien
Venus in visible light
Bildnachweis: NASA/JPL-Caltech credit link
License: PD Public Domain icons
Venus' surface
Bildnachweis: NASA/JPL credit link
License: PD Public Domain icons
Die Sterne und das Meer gemeinsam bewachen
Bildnachweis: Likai Lin/IAU OAU
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons Namensnennung 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) icons
Rumänischer Orion
Bildnachweis: Alex Conu/IAU OAE
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons Namensnennung 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) icons
A Matter of Perspective
Bildnachweis: Christofer Baez/IAU OAE (CC BY 4.0)
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons Namensnennung 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) icons
Phasen der Venus
Bildnachweis: Stephane Gonzales/IAU OAE (CC BY 4.0)
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons Namensnennung 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) icons
Jupiter, Venus, Moon Conjunction
Bildnachweis: Joslynn Appel/IAU OAE (CC BY 4.0)
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons Namensnennung 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) icons
Venus and Mercury Trails
Bildnachweis: Marcella Giulia Pace (CC BY 4.0)
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons Namensnennung 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) icons
Related Activities
Children's Planetary Maps: Venus
astroEDU educational activity (links to astroEDU website) Description: Learn more about our nearest neighbourLicense: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons Namensnennung 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) icons
Tags: Planetary cartography , Spatial thinking Age Ranges: 6-8 , 8-10 , 10-12 , 12-14 Education Level: Middle School , Primary , Secondary Areas of Learning: Social Research Costs: Low Cost Duration: 2 hours Group Size: Group Skills: Analysing and interpreting data , Asking questions , Communicating information , Constructing explanations , Developing and using models , Engaging in argument from evidence , Planning and carrying out investigations